Controller Area Network bus or CAN bus analysis is crucial for detecting the loss of important messages. In vehicle systems and many sophisticated embedded applications, preventing failures in the early development phase is an important demand of the market nowadays. CAN bus analysis can contribute to reducing development costs and especially to increasing the safety and efficiency of the system. Fraunhofer IESE’s CEP-CANdle tool aims to support such analysis and reveal open questions from the users of CAN bus architecture.
What is a Controller Area Network bus or CAN bus? How to prevent failures in the system?
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a widespread bus standard used for reliable data exchange between electronic control units (ECUs) in automobiles. Due to its simplicity and flexibility, CAN is used in trucks, buses, airplanes, industrial automation, submarines, and many other sophisticated embedded applications.
In hard real-time systems such as cars or airplanes, a deadline miss of a high-priority message may lead to huge damage or even loss of human lives. A reliable CAN schedulability test can predict potential worst-case deadline misses of CAN messages and thus prevent severe failures in the early development phase of an embedded system.
How does CEP-CANdle support Controller Area Network bus analysis?
Fraunhofer’s CEP-CANdle is a tool for CAN bus analysis that reveals open questions from the users of CAN bus architecture. Usually, the CAN bus architecture is specified in Vector’s DBC files, which define the ECUs and the CAN messages (and signals) shared among them. CEP-CANdle can perform static analysis based on DBC files, as well as dynamic analysis based on ASC files. Tools such as CANoe or the FERAL simulator can be used to check the functional behavior of a CAN bus by means of simulation. However, simulations cannot provide mathematical proof of the feasibility of CAN bus scheduling for all cases.
» Static Analysis – using DBC files
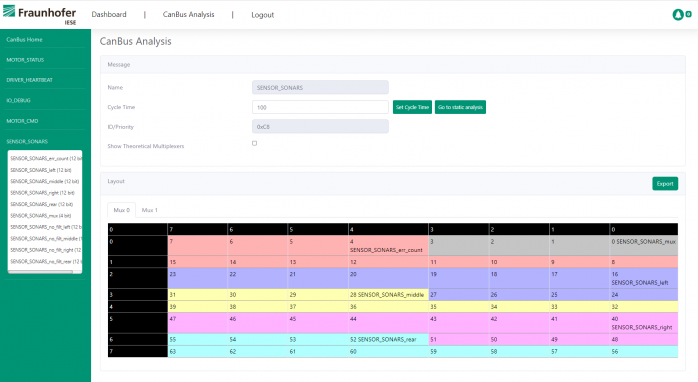
CEP-CANdle can perform a static analysis of the CAN bus scheduling and make a prediction as to whether a CAN message with a certain priority would have a deadline miss. In order to perform this static analysis, several steps are performed. First, CEP-CANdle parses a DBC file to gather information on all the CAN messages transmitted between the ECUs of a CAN bus. This information includes priority, period, deadline, and transmission time of a message. Second, the static analysis is carried out via mathematical calculation to predict the deadline misses in the worst case. Such an analysis is especially useful for detecting the loss of high-priority CAN messages where the CAN bus is heavily loaded.
Apart from performing static analysis, CEP-CANdle also uses DBC files to check the spare capacity in a CAN message payload. Especially in legacy systems, developers face the challenge of how to transmit information between two ECUs without creating new CAN messages. Therefore, it is important to quickly identify CAN messages that still have spare capacity in order to include an additional signal. CEP-CANdle can analyze a DBC file for CAN messages that still contain spare capacity, especially when multiplexer signals are used. With this ability, the developer can easily find CAN messages in the legacy system where the new signal can be defined.
» Dynamic Analysis – using ASC files
Additionally, CEP-CANdle can analyze a recorded ASC file from an HiL test setup. It will check for this recorded trace if all the messages and their periods follow the DBC specification. If a deadline miss occurs or a multiplexer is counted in a wrong way, the tool will inform the user. If the user compares the results generated by the static analysis and the analysis with the ASC file, they will find that the results are consistent. This shows that the static analysis provides the first-stage prediction of deadline misses before runtime. The analysis with the ASC file provides specific information on actual deadline misses at runtime. These two analyses provide great help for engineers to improve their bus design efficiently.
Which features does the CEP-CANdle tool offer?
CEP-CANdle is a web-based software tool that requires no local installation and is not machine-dependent. To use the tool, a browser is required, as well as an Internet connection and valid credentials (user and password). The tool provides flexibility regarding data storage and data privacy. Furthermore, it is possible to choose whether data is stored in Fraunhofer’s databases or in a private database. Besides the existing features of the tool, it is also possible to realize some customization in the tool.
In summary, the main features available in the CEP-Candle tool are:
- CAN scheduling analysis based on DBC definitions
- Easy detection of spare capacity in CAN messages, especially when multiplexers are used
- Transmission protocol from an HiL test analysis, which can detect faulty multiplexer signals
- Data control and flexibility to opt for either on-premise or shared private data solution
- Smart and interactive charts that provide visualization of CAN messages

