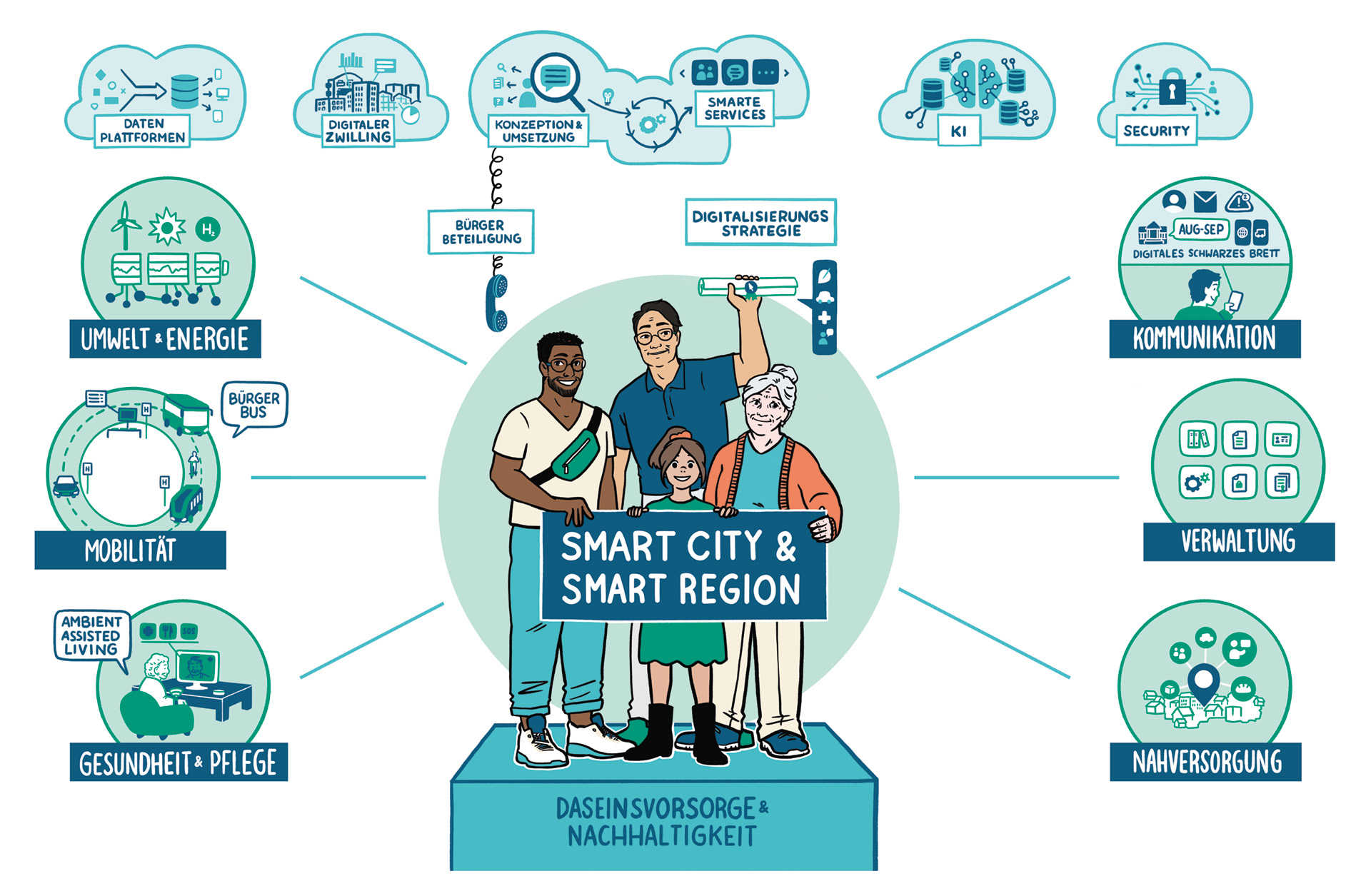
The smart community of the future
Digital transformation now permeates all areas of our lives – from administration and politics to mobility and security to health and communication.
Digital solutions offer immense potential for livable communities. Possible goals include the more sustainable use of resources, the digitization of administration, and the improvement of public services or citizen participation.
What is a smart city?
A smart city is a city that uses the potential of digitalization to become more modern and livable. The focus is on issues such as ecology, social coexistence, citizen participation, and many more. A smart region is a rural area that pursues the same goals.
The specific challenges faced by smart cities and smart regions differ significantly in some respects. We address both sides and can therefore respond to individual requirements.